Examining the Uses of Student-Led, Teacher-Led, and Collaborative Functions of Mobile Technology and Their Impacts on Physics Achievement and Interest

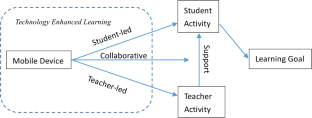
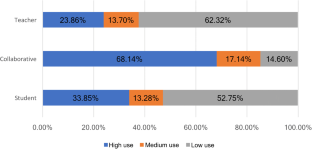
As mobile technology becomes more frequently used in science learning, understanding the relationship between student outcomes and the technology’s pedagogical features is drawing increasing attention. This study focuses on one pedagogical feature—“who led the use.” We first categorized 15 specific uses of mobile technology into three categories: student-led (i.e., initiated by the students and teachers have no or minimal influence on their use), teacher-led (i.e., initiated by teachers and the students have no or minimal impact on their use), and collaborative functions (i.e., both students and teacher need to play active roles in the use of mobile technology). We recruited 803 high school students who used a one-to-one tablet for 5 months and examined their use frequency, the functions used, and their physics outcomes. Results indicate a significant difference in the use frequency among the three categories. The collaborative functions were used with the highest frequency, whereas the student-led functions were used least. However, the student-led functions had a more significant effect size than the collaborative functions to predict both students’ physics achievement and physics interest, while teacher-led functions failed to predict either of these outcome variables.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save
Springer+ Basic
€32.70 /Month
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Buy Now
Price includes VAT (France)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Similar content being viewed by others
Understanding How the Perceived Usefulness of Mobile Technology Impacts Physics Learning Achievement: a Pedagogical Perspective
Article 17 August 2020
Using mobile technologies for mathematics: effects on student attitudes and achievement
Article Open access 23 February 2018
The Effect of Mobile Learning on School-Aged Students’ Science Achievement: A Meta-analysis
Article 11 November 2023
Explore related subjects
- Artificial Intelligence
- Digital Education and Educational Technology
References
- Ahmed, S., & Parsons, D. (2013). Abductive science inquiry using mobile devices in the classroom. Computers & Education, 63, 62–72. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Akcaoglu, M., & Bowman, N. D. (2016). Using instructor-led Facebook groups to enhance students’ perceptions of course content. Computers in Human Behavior, 65, 582–590. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Alpay, E., & Gulati, S. (2010). Student-led podcasting for engineering education. European Journal of Engineering Education, 35(4), 415–427. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Barron, B. (2000). Achieving coordination in collaborative problem-solving groups. Journal of the Learning Sciences, 9, 403–436. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Castropalacio, J. C., Velázquezabad, L., Giménez, M. H., & Monsoriu, J. A. (2013). Using a mobile phone acceleration sensor in physics experiments on free and damped harmonic oscillations. American Journal of Physics, 81(6), 472–475. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Crompton, H., Burke, D., Gregory, K. H., & Gräbe, C. (2016). The use of mobile learning in science: a systematic review. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 25(2), 1–12. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Davies, M. (2014). Using the Apple iPad to facilitate student-led group work and seminar presentation. Nurse Education in Practice, 14(4), 363–367. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Foshee, C. M., Elliott, S. N., & Atkinson, R. K. (2016). Technology-enhanced learning in college mathematics remediation. British Journal of Educational Technology, 47(5), 893–905. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12285. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- González, M. Á, González, M. Á, Llamas, C., Martín, M. E, Vegas, J., Martínez, Ó., Hernández, C., Herguedas, M. (2014). Mobile phones for teaching physics: using applications and sensors. Paper presented at the Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality. https://doi.org/10.1145/2669711.2669923.
- Groves, M. M., & Zemel, P. C. (2000). Instructional technology adoption in higher education: an action research case study. International Journal of Instructional Media, 27(1), 57–65.
- Hamilton, E. R., Rosenberg, J. M., & Akcaoglu, M. (2016). The Substitution Augmentation Modification Redefinition (SAMR) model: a critical review and suggestions for its use. TechTrends, 60(5), 433–441. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Han, I., & Shin, W. S. (2016). The use of a mobile learning management system and academic achievement of online students. Computers & Education, 102, 79–89. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Haya, P. A., Daems, O., Malzahn, N., Castellanos, J., & Hoppe, H. U. (2015). Analysing content and patterns of interaction for improving the learning design of networked learning environments. British Journal of Educational Technology, 46(2), 300–316. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Hochberg, K., Kuhn, J., & Müller, A. (2018). Using smartphones as experimental tools—effects on interest, curiosity, and learning in physics education. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 1–19.
- Huang, Y. M., & Chiu, P. S. (2015). The effectiveness of a meaningful learning-based evaluation model for context-aware mobile learning. British Journal of Educational Technology, 46(2), 437–447. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12147. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Ifenthaler, D., & Schweinbenz, V. (2013). The acceptance of tablet-PCs in classroom instruction: the teachers’ perspectives. Computers in Human Behavior, 29(3), 525–534. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Jonassen, D. H. (1991). Objectivism versus constructivism: do we need a new philosophical paradigm? Educational Technology Research and Development, 39(3), 5–14. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Jonassen, D. H., Peck, K., & Wilson, B. G. (1999). Learning with technology: a constructivist perspective. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Merrill. Google Scholar
- Karlson, A. K., Iqbal, S. T., Meyers, B., Ramos, G., Lee, K., & Tang, J. C. (2010). Mobile task flow in context: a screenshot study of smartphone use. International Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, CHI 2010, Atlanta, Georgia, USA, April, pp 10–15.
- Kershner, R., Mercer, N., Warwick, P., & Staarman, J. K. (2010). Can the interactive whiteboard support young children’s collaborative communication and thinking in classroom science activities? International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 5(4), 359–383. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Koroleva, D. (2016). Always online: using mobile technology and social media at home and at school by modern teenagers. Educational Studies, 1, 205–224. Google Scholar
- Kotrlik, J. W., & Redmann, D. H. (2008). A trend study: technology adoption in the teaching-learning process by secondary agriscience teachers—2002 and 2007. Journal of Agricultural Education, 50(2), 77–89. Google Scholar
- Lamb, R., Annetta, L., Meldrum, J., & Vallett, D. (2012). Measuring science interest: Rasch validation of the science interest survey. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 10, 643–668. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Lee, Y. J. (2010). Developing a mobile physics learning environment based on physics misconception research and E-Learning design principles. Journal of Computers in Mathematics & Science Teaching, 29(4), 399–416. Google Scholar
- Lin, T.-J., Duh, H. B.-L., Li, N., Wang, H.-Y., & Tsai, C.-C. (2013). An investigation of learners’ collaborative knowledge construction performances and behavior patterns in an augmented reality simulation system. Computers & Education, 68, 314–321. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Lindsay, L. (2016). Transformation of teacher practice using mobile technology with one-to-one classes: M-learning pedagogical approaches. British Journal of Educational Technology, 47(5), 883–892. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Liu, C.-Y., Wu, C.-J., Wong, W.-K., Lien, Y.-W., & Chao, T.-K. (2017). Scientific modeling with mobile devices in high school physics labs. Computers & Education, 105, 44–56. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Mac Callum, K., & Jeffrey, L. (2014). Factors impacting teachers’ adoption of mobile learning. Journal of Information Technology Education Research, 13(13), 141–162. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Makos, A., Lee, K., & Zingaro, D. (2015). Examining the characteristics of student postings that are liked and linked in a CSCL environment. British Journal of Educational Technology, 46(6), 1281–1294. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Palloff, R. M., & Pratt, K. (2002). Lessons from the cyberspace classroom: the realities of online teaching. John Wiley & Sons.
- Purba, S. W. D., & Hwang, W. Y. (2017). Investigation of learning behaviors and achievement of vocational high school students using a ubiquitous Physics Tablet PC App. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 26(3), 322–331. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Raudenbush, S. W., & Bryk, A. S. (2002). Hierarchical linear models: Applications and data analysis methods. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
- Reychav, I., & Wu, D. (2015). Mobile collaborative learning: the role of individual learning in groups through text and video content delivery in tablets. Computers in Human Behavior, 50, 520–534. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Romrell, D., Kidder, L. C., & Wood, E. (2014). The SAMR Model as a Framework for Evaluating mLearning. Online Learning, 18(2). https://doi.org/10.24059/olj.v18i2.435.
- Roschelle, J., & Teasley, S. D. (1995). The construction of shared knowledge in collaborative problem solving. In C. E. O’Malley (Ed.), Computer-supported collaborative learning (pp. 69–197). Berlin: Springer-Verlag. ChapterGoogle Scholar
- Ryu, S., Han, Y., & Paik, S. H. (2015). Understanding co-development of conceptual and epistemic understanding through modeling practices with mobile internet. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 24(2–3), 330–355. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Staver, J. R. (1998). Constructivism: sound theory for explicating the practice of science and science teaching. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 35(5), 501–520. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Tsai, C. (2001). The interpretation construction design model for teaching science and its applications to Internet-based instruction in Taiwan. International Journal of Educational Development, 21(5), 401–415. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Wette, R. (2015). Teacher-led collaborative modeling in academic L2 writing courses. ELT Journal, 69(1), 71–80. ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Zhai, X., Sun, W., Guo, Y., & Zhang, M. (2016). Smart Classroom: An evaluation of its implementations and impacts—Based on the longitude data of physics learning in a high school. China Educational Technology, 356(9), 121–127.
- Zhai, X., Li, M., & Guo, Y. (2018a). How learning progression-based formative assessment influences teachers’ instructional design: A case study of two teachers’ energy instruction. International Journal of Science Education. https://doi.org/10.1080/09500693.2018.1512772.
- Zhai, X., Zhang, M., & Li, M. (2018b). One-to-one mobile technology in high school physics classrooms: Understanding its use and outcome. British Journal of Educational Technology, 49(3), 516–532.
- Zhai, X., Zhang, M., Li, M., & Zhang, X. (2018c). Understanding the relationship between levels of mobile technology use in high school physics classrooms and the learning outcome. British Journal of Educational Technology. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12700.
- Zydney, J. M., & Warner, Z. (2016). Mobile apps for science learning: review of research. Computers & Education, 94, 1–17. ArticleGoogle Scholar
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for Lehong Shi, who helped with data analyses and also proofread the manuscript. The authors also thank Dr. Meilan Zhang for her generous help with the instrument design.
Funding
Author Xiaoming Zhai was supported by two grants from the Ministry of Education of China under Grant No. 13YJA880022 and No. DCA110195. Xiaoming Zhai was also funded by the Chinese Scholarship Council (No. 201506040139). Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the Ministry of Education of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Graduate School of Education, Stanford University, 520 Galvez Mall, CERAS Building 116, Stanford, CA, 94305, USA Xiaoming Zhai
- Department of Physics, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, 100875, China Xiaoming Zhai
- College of Education, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, 98195, USA Min Li & Siwei Chen
- Xiaoming Zhai





